From Challenges to Comfort: Palliative Care for Dementia Patients
Practical ways palliative care makes life more comfortable for dementia patients, addressing their physical and emotional needs with care.
The secret to beets’ heart-healthy reputation lies in their ability to boost nitric oxide levels in the body. Nitric oxide acts as a vasodilator, helping to expand blood vessels and improve blood flow.

Beets have come a long way from their humble roots, quite literally. They’re nutrient-dense and surprisingly versatile, lending themselves to everything from roasted vegetable dishes to salads to refreshing beetroot juice blends. A closer look into one of their core ingredients, nitrates, reveals why beets are so healthy and useful for your diet.
They’re simultaneously low in calories yet packed with essential nutrients like folate, manganese, potassium, and fiber. The greens, often discarded, boast their own impressive profile of vitamins A and K. However, beyond these basics, beets shine because of their bioactive compounds.

One such compound is betaine, an antioxidant that helps defend cells from damage, and another is a suite of pigments called betalains known for their anti-inflammatory properties. These nutrients contribute to the beet’s role as an anti-inflammatory food choice that may help reduce the risk of multiple chronic diseases. Yet, their true claim to fame lies in their influence on blood pressure, mediated through the body's conversion of nitrates to nitric oxide.
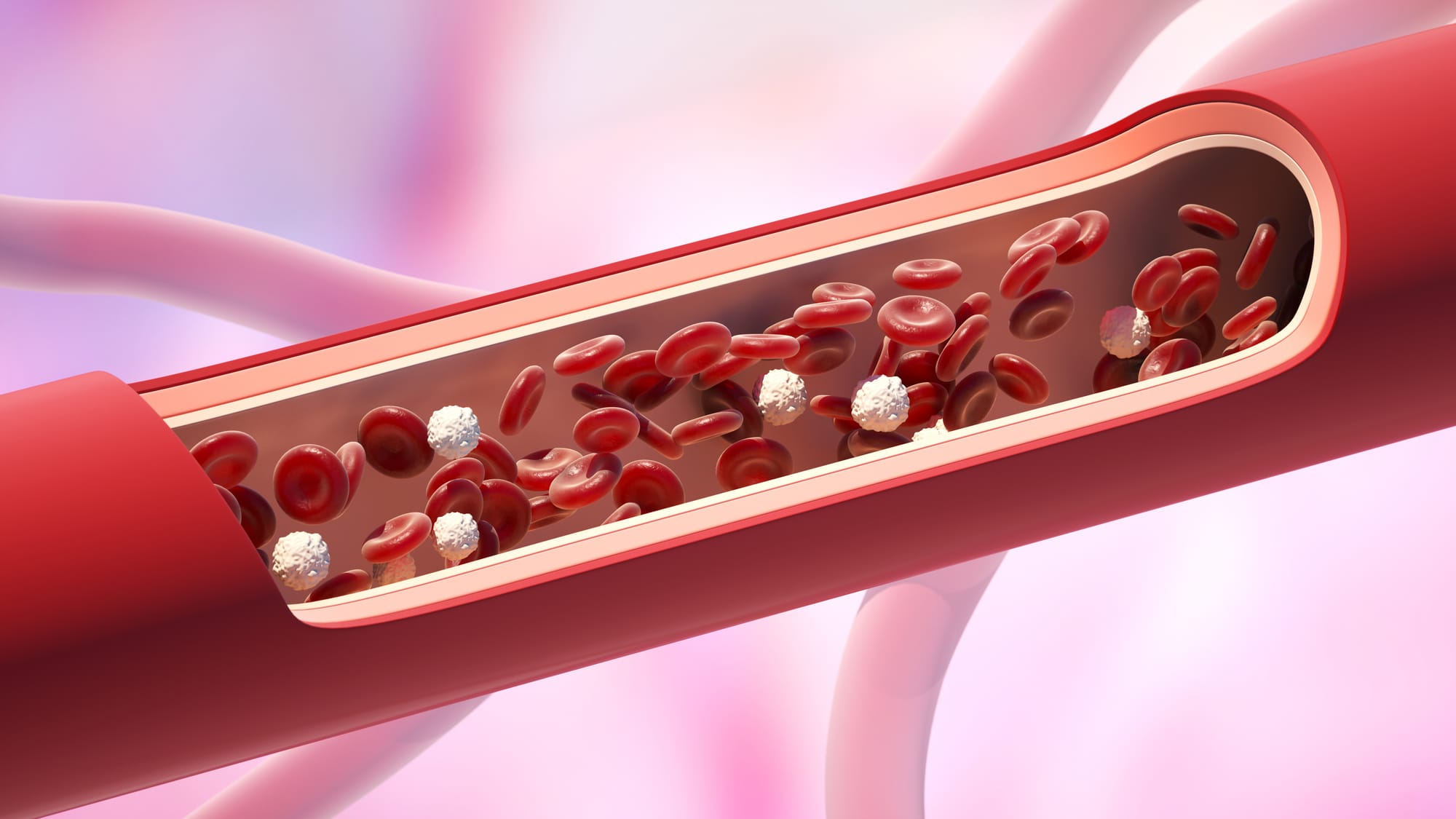
One of the most well-documented benefits of beets is their capacity to help lower blood pressure. The primary driver for this is beets role in the generation of nitric oxide, a molecule with extraordinary cardiovascular effects. Here's how the process unfolds:
Nitric oxide is far more than a mere byproduct of consuming nitrate-rich foods like beets; it’s a potent vasodilator crucial to cardiovascular health. By signaling the smooth muscle cells in blood vessel walls to relax, nitric oxide prompts these vessels to widen, facilitating easier and more efficient blood flow. This process, known as vasodilation, significantly lowers the pressure inside the arteries, reducing strain on the heart and optimizing blood circulation.
The importance of nitric oxide lies in its ability to maintain vascular flexibility, a fundamental factor for healthy blood pressure and effective circulation. When blood vessels remain pliable and open, the heart doesn’t need to work as hard to deliver oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. This reduction in cardiovascular strain is vital for overall heart health, highlighting nitric oxide’s role as a key molecule in supporting a resilient and well-functioning vascular system.
The impact of beetroot and beetroot juice on blood pressure has been the focus of numerous studies, with results that continue to affirm beets' cardiovascular benefits:
Current research suggests that consuming about 250 mL (roughly 8.5 ounces) of beetroot juice daily can produce measurable blood pressure-lowering effects. This dosage appears to be effective and well-tolerated for most people, though individual responses may vary. It's worth mentioning that for people who dislike the earthy flavor of beetroot juice, there are other creative ways to incorporate beets into the diet, such as roasted beets in salads or beet hummus.

While nitric oxide's role in blood pressure regulation is the main goal, beets' benefits extend further. The vasodilation effect of nitric oxide also improves blood flow to the brain, potentially enhancing cognitive function. In older adults, this could mean better mental sharpness and a reduced risk of dementia. Athletes, too, have found a use for beets: improved oxygen use during exercise has been linked to higher stamina and performance, making beetroot juice a popular pre-workout drink.
Additionally, the fiber in beets supports a healthy gut, which plays a critical role in overall wellness. With a balanced digestive system, nutrient absorption improves, inflammation may decrease, and immunity is strengthened.

Despite the many benefits, beets aren’t a cure-all. People on medication for hypertension should never replace prescribed treatments with dietary interventions without consulting a healthcare provider. Moreover, some individuals may notice their urine turning pinkish—a harmless phenomenon known as beeturia. Those prone to kidney stones may also need to moderate beet consumption due to high oxalate content.