From Challenges to Comfort: Palliative Care for Dementia Patients
Practical ways palliative care makes life more comfortable for dementia patients, addressing their physical and emotional needs with care.
Aging often brings unique health challenges, from arthritis to cardiovascular disease. With the right medical care and practical lifestyle adjustments, older adults can manage these conditions and maintain a fulfilling life.

Aging often brings an array of chronic health conditions, many of which are closely linked to lifestyle. From managing cardiovascular health to addressing cognitive changes, targeted lifestyle adjustments can play a powerful role in reducing symptoms and improving quality of life. Here’s an in-depth look at ten of the most common chronic health issues in older adults, along with evidence-based lifestyle changes that support clinical treatments.
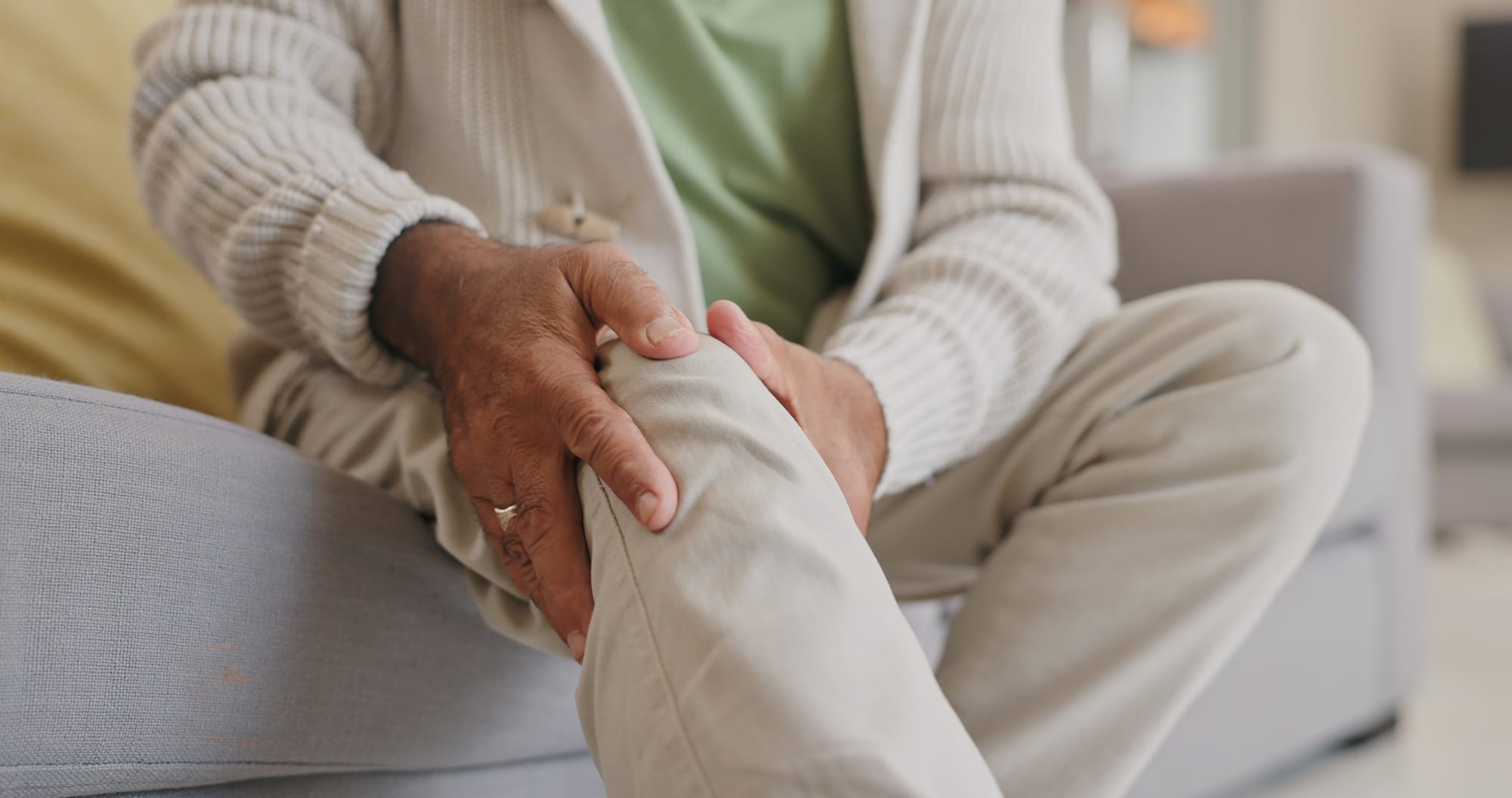

Overview: Osteoarthritis (OA) results from cartilage wear and tear, while rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease causing chronic joint inflammation. The CDC reports that over half of all respondents surveyed over the age of 65 suffer from some form of arthritis.
Management Approaches: Treatment for OA focuses on physical therapy, weight management, and analgesics. RA management includes disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologics to control immune-mediated inflammation.
Lifestyle Modifications:
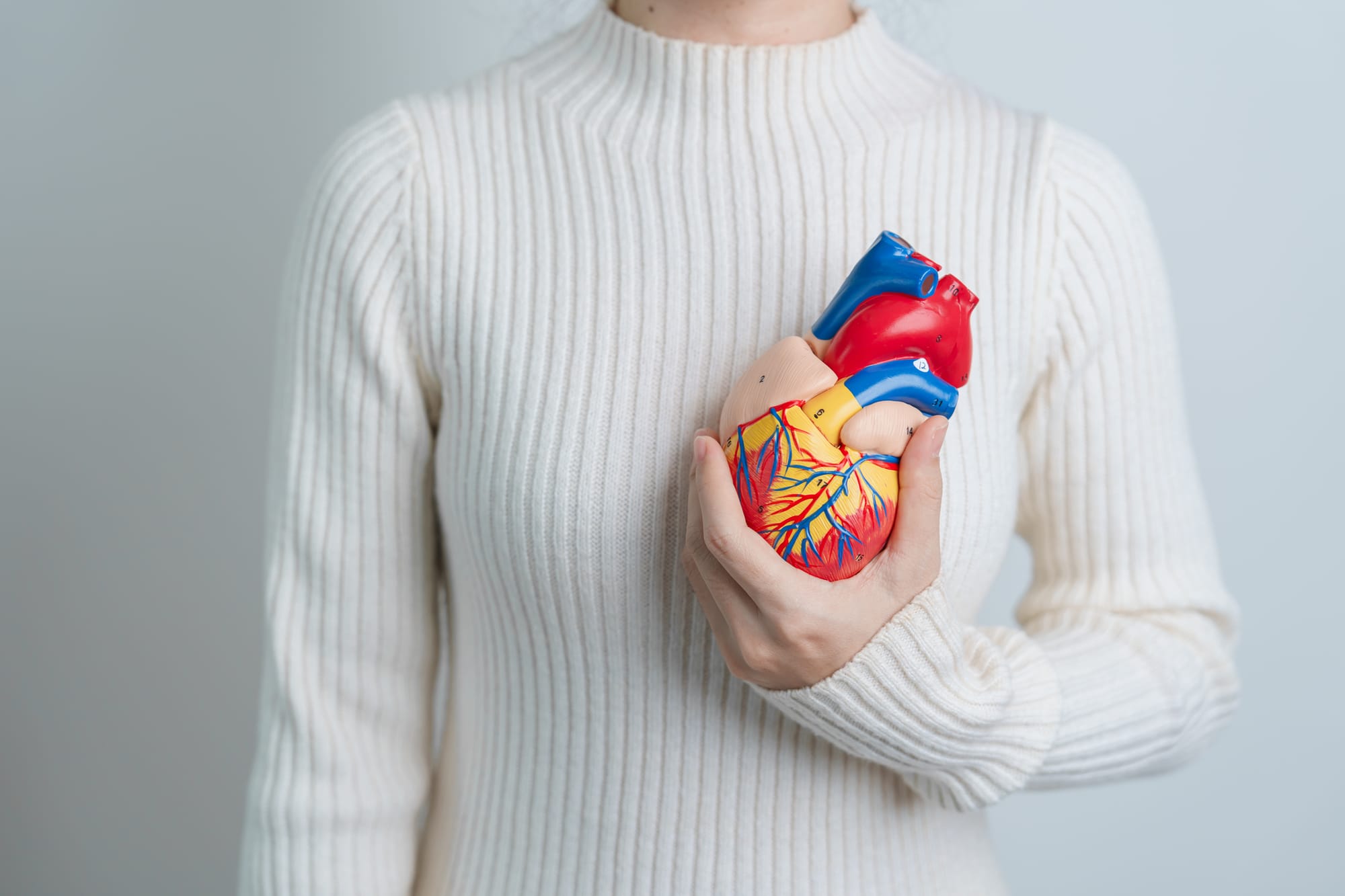

Overview: CVD encompasses coronary artery disease (CAD), heart failure, and arrhythmias. According to a recent report by the American Heart Association, approximately 61% of U.S. adults (about 6 in 10) are projected to have some form of cardiovascular disease by 2050.
Preventive and Therapeutic Interventions: CVD prevention involves lifestyle modification, including diet and exercise, pharmacotherapy (e.g., statins, beta-blockers), and routine cardiovascular screenings to manage modifiable risk factors.
Lifestyle Modifications:
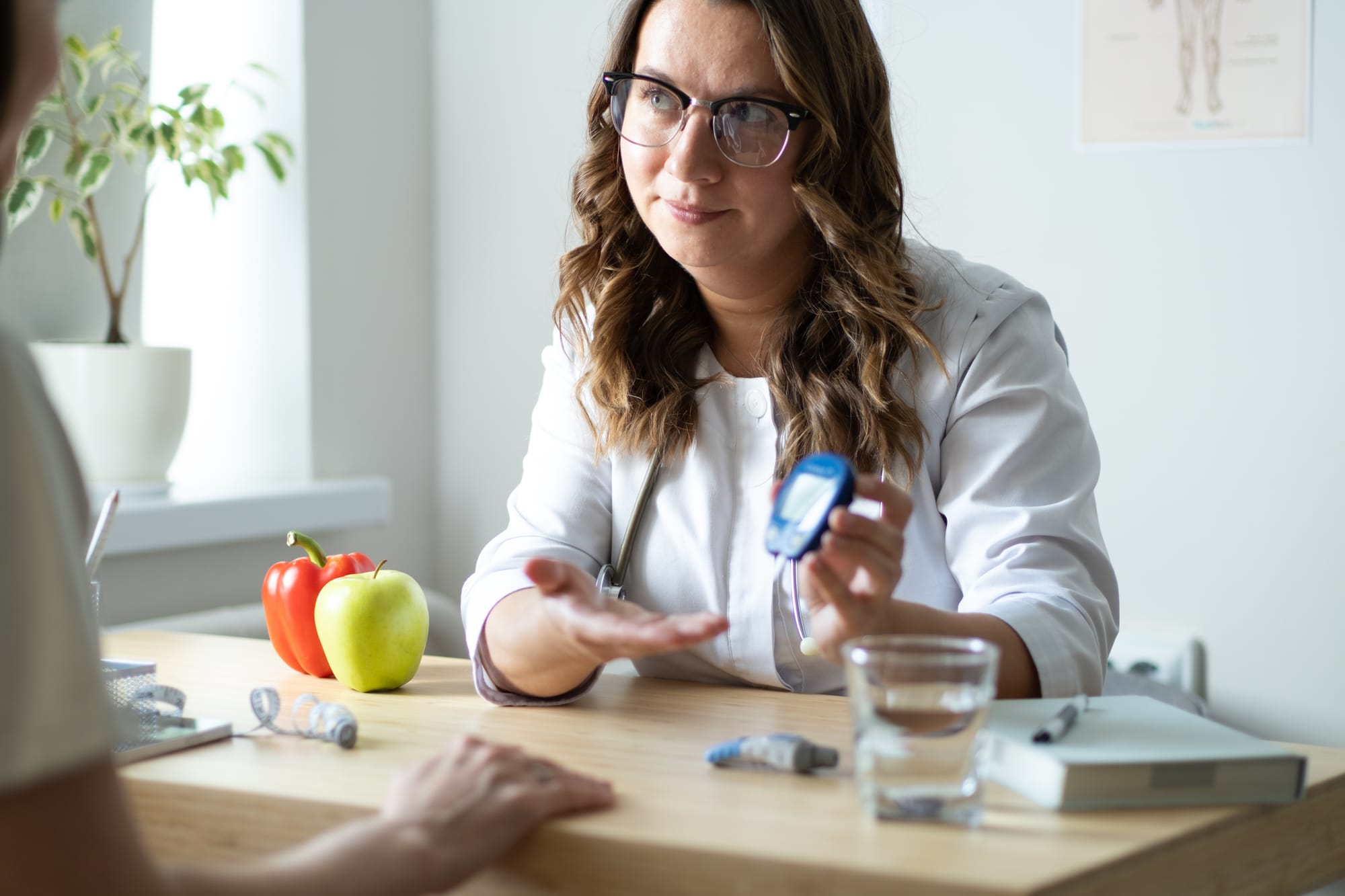

Overview: Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) results from insulin resistance and impaired glucose regulation. The CDC's National Diabetes Statistics Report 2022 states that 26.8% of adults aged 65 and older have diabetes.
Complications and Clinical Management: T2DM increases the risk of complications, such as nephropathy, neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease. Effective management includes dietary adjustments, physical activity, and pharmacological interventions like metformin and insulin therapy as needed.
Lifestyle Modifications:
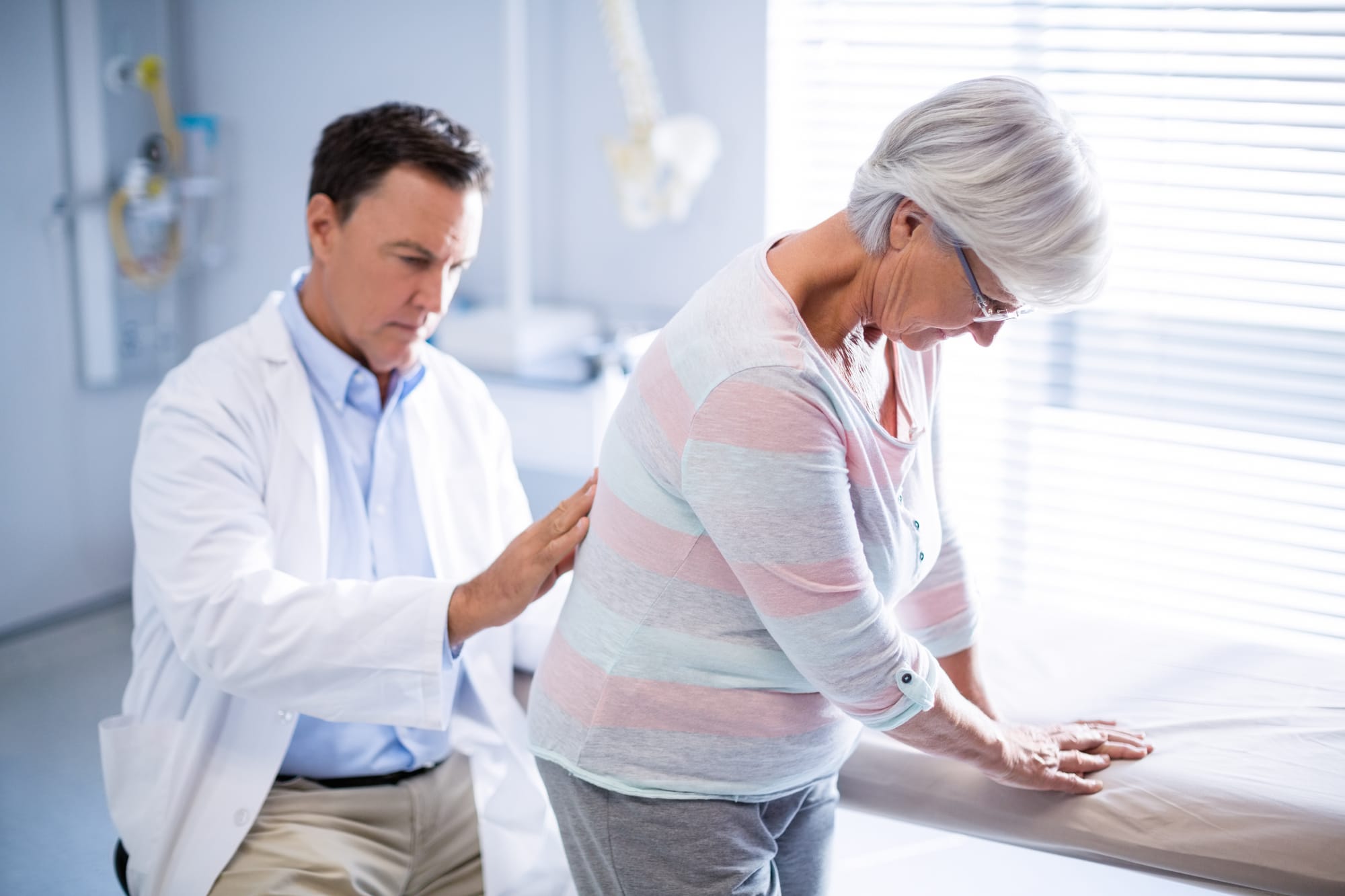

Overview: Osteoporosis leads to reduced bone density, increasing fracture risk. Osteoporosis affects about 14 million people in the U.S., with 80% of those affected being women. It’s particularly common in older adults, with around 54 million Americans at risk due to low bone density.
Prevention and Treatment Options: Bone density screenings (DEXA scans) aid in early diagnosis. Management includes calcium and vitamin D supplementation, bisphosphonates, and physical therapy focused on resistance training to enhance bone strength.
Lifestyle Modifications:

Overview: COPD includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, often related to long-term smoking or pollutant exposure. The American Lung Association states that approximately 5% of adults or 12.5 million Americans are living with COPD.
Management and Treatment Modalities: Management includes bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and oxygen therapy. Pulmonary rehabilitation and breathing exercises are crucial for improving respiratory function and quality of life.
Lifestyle Modifications:

Overview: Alzheimer’s and other dementias involve progressive cognitive decline due to neuronal loss and brain atrophy. The Alzheimer's Association's 2023 report estimates that 6.7 million Americans 65 and older are living with Alzheimer's dementia in 2023.
Management and Supportive Care Strategies: Treatment is focused on symptom management, as there is no cure. Cholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists may provide modest cognitive benefits. Structured routines and caregiver support are essential for patient well-being.
Lifestyle Modifications:

Overview: Older adults often experience depression and anxiety due to isolation or life changes. A CDC report finds that in 2020, 18.4% of US adults reported having ever been diagnosed with depression in their lifetimes.
Treatment and Support: Psychotherapy, pharmacotherapy (SSRIs), and lifestyle interventions are effective. Social support networks, activity engagement, and counseling contribute to improved mental health outcomes.
Lifestyle Modifications:

Overview: Cancer risk, including breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers, increases with age. According to the American Cancer Society, in 2023, 1,958,310 new cancer cases are projected to occur in the United States.
Treatment and Management: Treatment considerations for older adults include balancing efficacy with quality of life, as many cancers in this population are slow-growing. Radiation, chemotherapy, and surgical interventions are tailored to individual needs and tolerability.
Lifestyle Modifications:
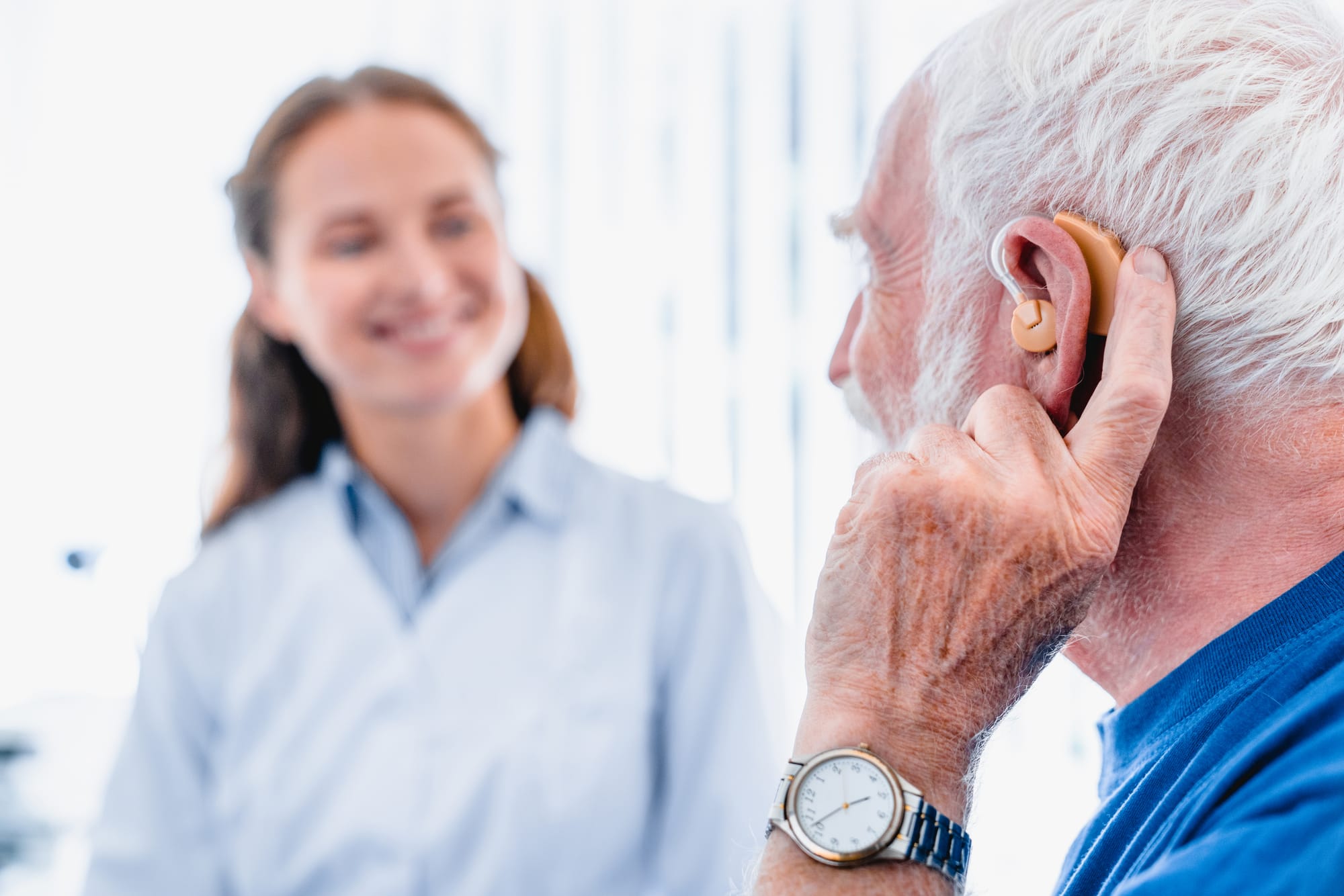

Overview: Age-related macular degeneration, cataracts, and presbycusis (age-related hearing loss) are common. A recent study estimates that 65.3% of adults 71 years and older (representing 21.5 million individuals) had at least some degree of hearing loss.
Management and Assistive Solutions: Corrective lenses, cataract surgery, and hearing aids provide practical solutions. Low-vision and audiology services further support adaptation to sensory impairments.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Overview: CKD results from conditions like diabetes and hypertension, leading to impaired kidney function. The National Kidney Foundation reports that 37 million American adults are estimated to have CKD.
Management Strategies: Management includes blood pressure control, dietary modifications, and monitoring electrolyte levels. ACE inhibitors and ARBs are commonly prescribed to slow progression, and regular nephrology consultations are recommended.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
Chronic conditions like these pose unique challenges in aging, but proactive management and preventive measures can improve outcomes and preserve function. Early detection, lifestyle adjustments, and a coordinated care approach involving healthcare providers and caregivers are essential to managing these health issues in older adults effectively. Through these steps, older adults can navigate chronic health conditions with a focus on maintaining quality of life and independence.